In this article, we hope to clarify some of the confusion that our Eason and Tambornini spinal cord attorneys regularly hear from clients. We will help you understand the different levels of spinal cord injuries, as well as the different grades of a spinal cord injury. The two should not be confused, though, since they are not the same. When you say spinal cord level, it pertains to the location of the injury. Spinal cord grade, on the other hand, pertains to the severity of the injury.
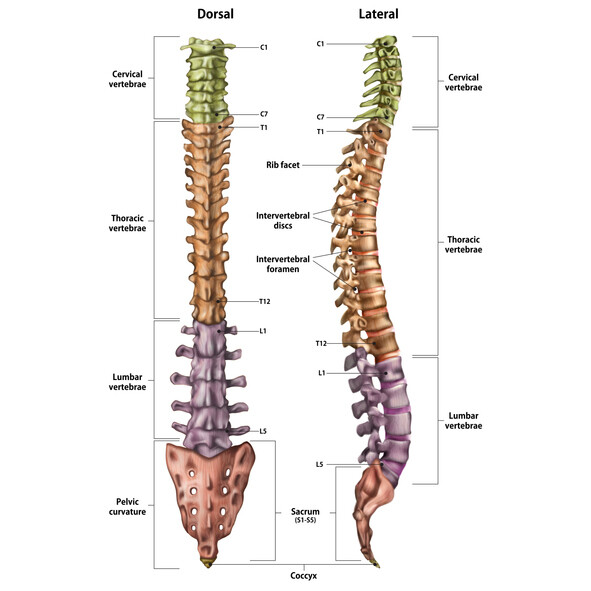
Our spine is a series of vertebras divided into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions. The spinal cord is located inside the vertebras and runs down the length of the spine. Along its sides are 31 pairs of spinal nerves.
There are eight cervical nerves (C1 to C8), 12 thoracic nerves (T1 to T5), five lumbar nerves (L1 to L5), five sacral nerves (S1 to S5), and one coccygeal nerve (Co1). The letters correspond to the type of spinal nerve. The numbers, on the other hand, correspond to the vertebra where the spinal nerve exits. The main job of the spinal nerves is to relay signals (both sensory and motor) from the body to the brain and vice versa.
Each spinal nerve pair provides sensory and motor functions to a specific body region:
- C1 through C8 spinal nerves supply the head, neck, and upper extremities. Upper cervical nerves (C1 through C4) also supply the diaphragm, which is the muscle for breathing.
- T1 through T12 spinal nerves supply the chest, abdomen, and mid-back.
- L1 through L5 spinal nerves supply the lower abdomen and the lower extremities.
- S1 through S5 spinal nerves also supply the lower extremities as well as the pelvic region.
- Co1 spinal nerve supplies the genital and rectal areas.
Spinal cord injury is named based on the section or level of the injured spine. Injury to the spinal cord and spinal nerves at these levels cause loss of function to the areas they supply. For example, injury to the spinal cord at the level of the cervical spine results in paralysis and loss of sensation in the neck, upper extremities, and lower extremities. It can also result in the inability to breathe on their own or control their bowel or bladder functions.
Injury to the spinal cord at the level of the lumbar or sacral spine often results in loss of function of the hips as well as the lower extremities. Depending on the severity of the injury, the patient may be able to walk with the use of assistive devices like wheelchair, braces, and crutches. They also may have some form of control over his bowel and bladder functions.
Spinal cord injury is also classified according to the grade or severity of the injury. Grade A is categorized as the most severe, while Grade E is the least severe.
- Grade A means there is a complete loss of sensory and motor functions below the level of the injury.
- Grade B means there is a loss of motor function below the level of the injury, but sensory function is preserved.
- Grade C means that there is preservation of the sensory and motor functions below the level of the injury. However, the muscle grade of more than half of the patient’s major key muscles is below 3. He can move his limbs on a horizontal plane but has difficulty moving it against gravity.
- Grade D means that there is preservation of the sensory and motor functions below the level of the injury. However, the muscle grade of more than half of the patient’s major key muscles is above 3. He can move his limbs through their full ranges of motions against gravity and with moderate resistance.
- Grade E means normal sensory as well as motor functions.
Muscle grades are classified into:
- 0 (None) means no muscle contractions can be felt or seen.
- 1 (Trace) means there is no motion, but muscle contractions can be felt or seen.
- 2 (Poor) means there is partial movement, but only if gravity and resistance are eliminated.
- 3 (Fair) means there is full range of motion against gravity.
- 4 (Good) means there is full range of motion against both gravity as well as moderate resistance.
- 5 (Normal) means there is full range of motion against both gravity as well as maximum resistance.
When both upper and lower extremity motor functions are affected, the condition is called quadriplegia or tetraplegia. The patient will need full support and assistance in his mobility and activities of daily living. He will also need special equipment for bladder and bowel functions.
When the upper extremities are normal, and only the lower extremities are affected, the condition is called paraplegia. The patient can learn to use assistive devices for his mobility as well as learn new skills to gain independence. He may or may not need special equipment for his bladder and bowel functions, depending on the level of his injury.
Treatment for spinal cord injury begins in its early or acute phase. The patient is immobilized to protect the injured spine and prevent further damage. At the same time, the patient is also given medications to maintain normal physiological parameters and reduce inflammation in the spine, which further contributes to spinal cord injury. Depending on the severity of the injury, surgery may be given to remove bone fragments, reduce spinal cord pressure, and repair torn ligaments, discs, muscles, etc.
Spinal cord injury patients need intensive treatment, care, and therapy. Physical therapy and rehabilitation start as soon as possible to prevent complications and help improve prognosis. He is also taught how to use assistive devices to become more independent.
Prognosis depends on the level and completeness of the injury. Those who have a high level, Grade A, complete spinal cord injury typically have a poor prognosis and less chances of motor recovery, compared to those with incomplete injuries and lower level spinal cord injury.
What can you do?
Spinal cord injuries are obviously some of the most severe injuries someone can suffer. They are also very expensive, especially if the damage is extensive and permanent. If you have suffered a spinal cord or spinal column injury or are researching on behalf of someone who has, we hope you will reach out to one of our Eason and Tambornini spinal cord injury attorneys for more information and a free consultation. We help patients who sustained spinal cord injury at work or caused by a negligent third party or an accident. So send us a message now or give us a call, and our Eason and Tambornini spinal cord injury attorney in Sacramento will assist you in exploring your legal options.

